Define each term below in terms of solute. Anatomy and physiology questions and answers.
3 Eso Osmosis Process In Cells | Silviapvadi's Blog
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes than the cytoplasm of a cell, that solution is hypotonic to the cytoplasm.
Which way will water move in a hypotonic solution. The water, driven to equalize the two. A cell with a cytosol that is a hypotonic solution to the environment will lose water to the more hypertonic environment that has more solutes. The direction of the flow continues until the solutions are.
Which way will water move? The cell expands as water moves in. You can assume that the additional space surrounding the solutes is water and that the tan area is inside the cell.
This will cause the fluids to move inside the cell, resulting in the expansion or swelling of. If the solute concentration outside the cell is lower than inside the cell,. A hypotonic solution has a lesser solute concentration than that in the cell.
The list of hypotonic solutions is easy to remember, because it really only includes one true hypotonic solution (plus one “faker”): The power of an extracellular solution to allow water to move in or out of a cell through osmosis is called ‘tonicity’. The list of hypotonic solutions is easy to remember, because it really only includes one true hypotonic solution, plus one “faker”:.
*5% dextrose in water (this is. A solution whose concentration is more than the cell. Hypertonic solution is a more.
Predict what will happen when you place a cell in a hypertonic solution. The solute concentration for the second solution is 80% with a solvent concentration of 60%. Thus, the water molecules move inside the cell from outside.
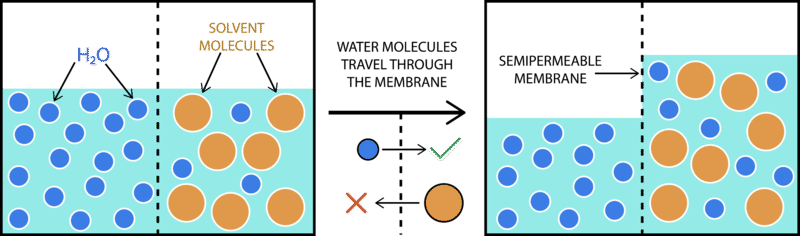
Water moves from the hypotonic (less concentrated) side of a membrane to the hypertonic (less concentrated) side. A solution whose concentration is less than the cell sap or inside of a cell. If a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, there will be a net flow of water into the cell, and the cell will gain volume.
Hypertonic solutions will move water from the cells into the vessels (extracellualr) and hypotonic solution will move water from fluid from the vessels into. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will move from outside the cell where there is a low. The difference between the number of dissolved solids creates an osmotic pressure gradient that forces water to move to achieve equilibrium between the inside and outside.
The solute concentration of the first solution is 30% with a solvent concentration of 60% nacl. Draw the appearance of red. A solution’s tonicity relates to its osmolarity.
Examples of hypotonic iv fluids.
Osmosis - Advanced | Ck-12 Foundation
What Happens To A Cell In A Hypotonic Solution, With Regard To Water Content? Why? - Quora