Because of symmetry constraints, i.e. The extra energy produced by the ring orbitals of the delocalized electrons from the “pi” bonds that are spread out over the entire covalently bound molecule is referred to as.
Delocalisation | Facts, Summary & Definition | Chemistry Revision
This time there are only four orbitals.

Orbitals of delocalized pi bonds. This can be seen in. If they supply 90% or 99% or 99.9% of the solution, is. Localized electrons exhibit normal behavior, a localized lone pair remains close to one atom, and a localized bond pair travels between two atoms.
These bonds form due to frontal overlapping between s orbitals, p. Delocalized pi bonds are the pi bonds that are shared between three or more atoms in which the electrons move freely over more than two atoms. Consequently, the molecular orbital approach, called molecular orbital theory, is a delocalized approach to bonding.
A pi bond has one nodal plane that is parallel to the bond axis (the axis passing both nuclei of the chemical bond), thus cannot be formed by s orbital that lacks any angular node. In a molecule like ethylene, the electrons in the π bond are constrained to the. In most cases, a small number of orbitals supply most of the solution, and can be individually considered as “bonds”.
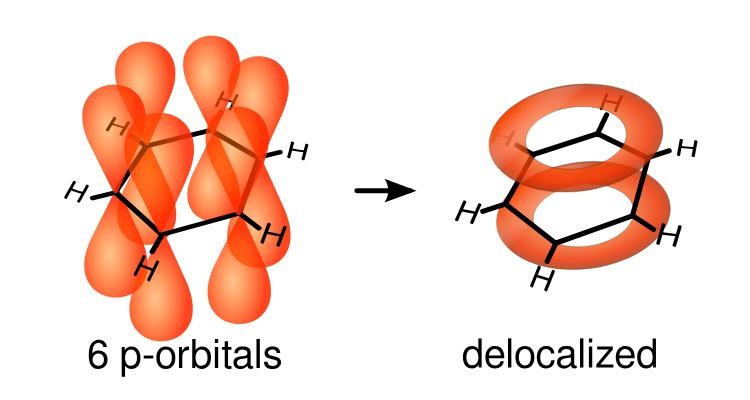
In a molecule like ethylene, the electrons in. This allows the pi electrons to be delocalized in molecular orbitals that extend all the way around the ring, above and below the plane. Delocalisation energy is the extra energy provided by the ring orbitals of the delocalized electrons, from the “pi” bonds, that are spread out over the whole covalently bonded molecule.
The valence electrons of the interacting metal atoms’ s and p orbitals delocalise in metallic bonds. A delocalized π bond is a π bond in which the electrons are free to move over more than two nuclei. Localised chemical bonds are normal sigma and pi bonds or lone electron pairs that exists on a single atom.
Nov 20, 2016 a delocalized π bond is a π bond in which the electrons are free to move over more than two nuclei. I think delocalized pi bonds occur as unhybridized p orbitals may overlap and the electrons are not localized to a specific atom; For this to happen, of course, the ring must be.
That is, instead of orbiting their respective metal. In which bonds are electrons delocalised? Therefore the electrons are expected to be exchanged in between individual.
Note the pattern molecular orbital theory is a delocalized bonding.
11.6: Delocalized Electrons: Bonding In The Benzene Molecule - Chemistry Libretexts

30.01 Structural Elements Of Delocalized Pi Systems - Youtube