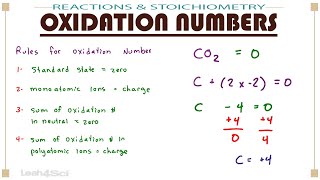
The iodine has been oxidized. The total of all the atoms in a molecule’s oxidation numbers equals zero.
How Can I Assign Oxidation Numbers To Each Of The Atoms? | Socratic
This video walks you through redox pairs using the mnemonic leo the lion says ger to help you understand oxidizing/reducing agents.
How to find oxidation number math. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero. B) the oxidation state of charged ions is equal to the net charge of the ion. Oxidation number of a free element is zero.
Finding the oxidation number of elements, ions,. The oxidation number of an atom in an oxygen molecule is zero. Group 1 element oxidation number in a compound.
The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. We go from a plus seven to a plus four. Click here to access solved previous year questions, solved examples and important formulas based on the chapter.
You’ll also learn how to recognize (rather than memorize) common oxidizing and reducing agents. Jee preparation requires clarity of concepts in how to find oxidation number. Oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion.
How to update my profile? Different ways of displaying oxidation numbers of ethanol and acetic acid. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 84,000 lessons in math, english, science, history, and more.
The sum of all oxidation states. The oxidation number of a free element is always 0. In kmno 4, the oxidation number of k is +1, the oxidation number of mn is +7 and the oxidation number of oxygen is −2.
To determine if electrons were gained or lost by an atom, we assign an oxidation number to each atom in a compound. Now let's look at the manganese. So to go from an oxidation number of negative one to zero, you need to lose electrons.
There are some basic rules: Exceptions are peroxides, super oxides and compounds with fluorine. Add math in forum posts;
Na = 1(1) = 1 n a = 1 ( 1) = 1 since o o is in column 6 6 of the periodic table, it will share 6 6 electrons and use an oxidation state of 6 6. Oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to charge of that ion. When one atom loses electrons, another atom has to gain these electrons.
Knowledge of the following criteria can be used to calculate the oxidation number of elements in compounds. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. Bonds between atoms of the same element (homonuclear bonds) are always divided equally.
We go from an oxidation number of negative one to zero. How to assign oxidation numbers to the atoms in a molecule. Oxidation number of hydrogen in hydrogen chloride (hcl) is + 1.
Our oxidation number has gone down. Rules to compute the oxidation numbers 1. So it has been oxidized.
Add video in forum posts; How to update billing info; The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion, for instance, na+ = +1;
The sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in a given compound is zero (for a neutral compound), or equal to the charge on the compound (for compounds that have a charge). Let me write that down. The oxidation number of a free element is always 0.
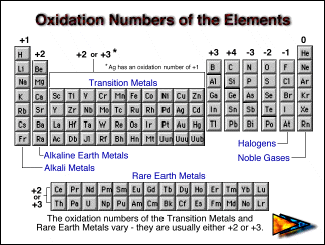
So, oxidation number of all alkali metal ions is always = +1 oxidation number of all alkaline earth metal ions is always = +2 oxidation number of all boron family metal ions is always = +3 To find oxidation number the following are the basics, the oxidation number of a free element is always 0. The oxidation number of each atom can be calculated by subtracting the sum of lone pairs and electrons it gains from bonds from the number of valence electrons.
The highest possible oxidation number of an element is its group number, and the lowest possible oxidation number is its group number minus 8.

Grade 12 Chemistry: Finding Oxidation Numbers] How Do You Find The Oxidation Numbers For Metals In A Molecule? : R/Homeworkhelp

Oxidation Number Rules & Examples | What Is An Oxidation Number? - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com