Ρh2 = p rt × 2.016 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1. Also included are two practice problems using d=mp/nrt and d=mp/rt including molar mass a.
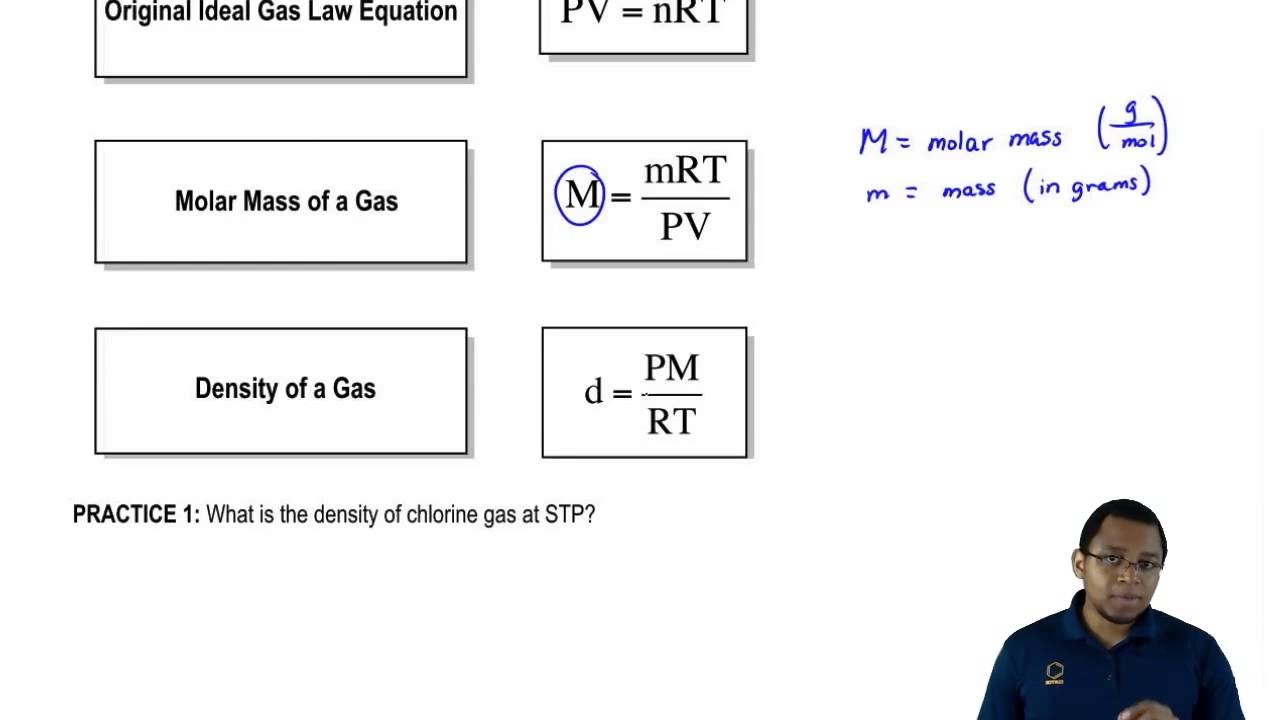
Using The Ideal Gas Law To Find Density Or Molar Mass - Youtube
Math geometry physics force fluid mechanics finance loan calculator.

Density in gas law. Combined with avogadro's law (i.e. This means that at an unchanged temperature and pressure conditions, the molar mass of every gas is directly proportional to its density. The temperature in tank is 70 of.
Graham's law states that the rate at which gas molecules diffuse is inversely proportional to the square root of the gas density at constant temperature. The density d of a gas, on the other hand, is determined by its identity. The density of gases can be computed using the ideal gas law.
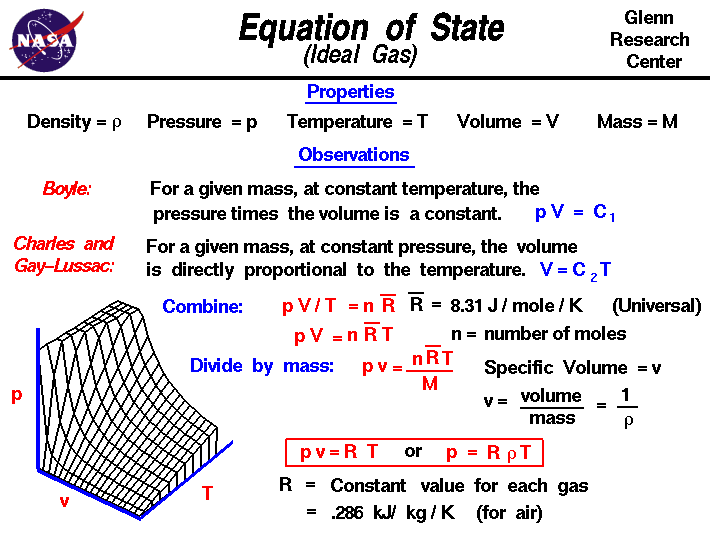
Density = total mass total volume = n 1 m 1 + n 2 m 2 ( n 1 + n 2) r t / p = p ( n 1 m 1 + n 2 m 2) ( n 1 + n 2) r t = p m avg r t. Gas density is defined as the mass of the gas occupying a certain volume at specified pressure and temperature. The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas.it is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations.
The ideal gas law is applicable for gases that have the following characteristics: The chemical formula as well as molar mass has also been listed. I do not understand what you're denoting by m r.
O r]* (70+ 460) [°r]) = 0.0102 [slugs/ft3] the weight of the air is the product of specific weight and the air volume. Since equal volumes have equal number of molecules) this is the same as being inversely proportional to the root of the molecular weight. Substitute the correct values into this equation and you're good to go.
Density is defined as mass per unit volume. The collisions between the gas particles are. Multiplication of the left and right sides of equation 5.5.1 by the molar mass in g/mol ( m) of the gas gives (5.5.2) ρ = g l = p m r t this allows us to determine the density of.
Density of a gas is generally expressed in g/l (mass over volume). In addition, the density of a gas is equal to its mass divided by its volume. We note that hydrogen gas, as are all elemental gases.
And recall that volume percent is equivalent to mole percent, as you correctly did already. Ρ = pm/rt, where m is molar mass. How to find density of a gas calculating the density of a gas usually involves combining the formula for density (mass divided by volume) and the ideal gas law (pv = nrt).
The air density can be calculated with a transformation of the ideal gas law (5) to: With this information we can calculate the density () of a gas using only its molar mass. The above gas laws provide us with an indication of the various properties of gases at changed conditions of temperature, pressure volume and mass.
The ideal gas law is pv = nrt, so if you know enough values, you can calculate volume (v) or the number of moles (n). The density is usually represented in units of lbm/ft3. Moreover, you can calculate the molar mass of a substance once you know the density of a gas.
Below the table is an image version for offline viewing Density, mass of a unit volume of a material substance. Density is the ratio of mass over volume.
What is gas density and how does it fit mathematically into pv=nrt? The ideal gas law is universal, relating the pressure, volume, number of moles, and temperature of a gas regardless of the chemical identity of the gas: Sometimes you then have to convert number of moles to grams.
Ideal gas law equations calculator science physics chemistry formulas. In other words, 1 mole of a gas will occupy 22.4 l at stp, assuming ideal gas behavior. = 1 ⋅ atm ×2.016 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1 0.0821 ⋅ l⋅atm k⋅mol × 298 ⋅ k ≅0.1 ⋅ g ⋅ l−1.
Ρ = p / (r t) (7) ρ = ( (50 [lb/in 2 ]+ 14.7 [lb/in 2 ])*144 [in 2 /ft 2 ]) / (1716 [ft.lb/slug. Noting that m/v is density, ρ, the equation can be written as p (mw) = (m/v)rt = ρrt. Solving for ideal gas density.
And thus our working equation. The ideal gas law is a. Gas density is a function of the pressure and temperature conditions for the gas.
Another common density representation is the “gas gradient” that is expressed in units of psi/ft. What is the formula for calculating density? At stp, the volume of a gas is only dependent on number of moles of that gas and is independent of molar mass.
First, starting with the definition of density Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for density given pressure, specific gas constant and temperature. Density of gas we can define it as the mass per unit volume of a substance under specific conditions of temperature and pressure.
Mass v density=ρ = p rt ×molar mass. We can introduce the density of the gas into the equation by making use of the fact that molecular weight (mw) has units of mass/mole, and thus that n = m/mw, and that the ideal gas law can be written as: