= 1 ⋅ atm ×2.016 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1 0.0821 ⋅ l⋅atm k⋅mol × 298 ⋅ k ≅0.1 ⋅ g ⋅. The gas consists of a large number of molecules that move around randomly.
Ppt - Equation Of State (A.k.a. The “ Ideal Gas Law ” ) Powerpoint Presentation - Id:2230613
What is the density standard for gases?
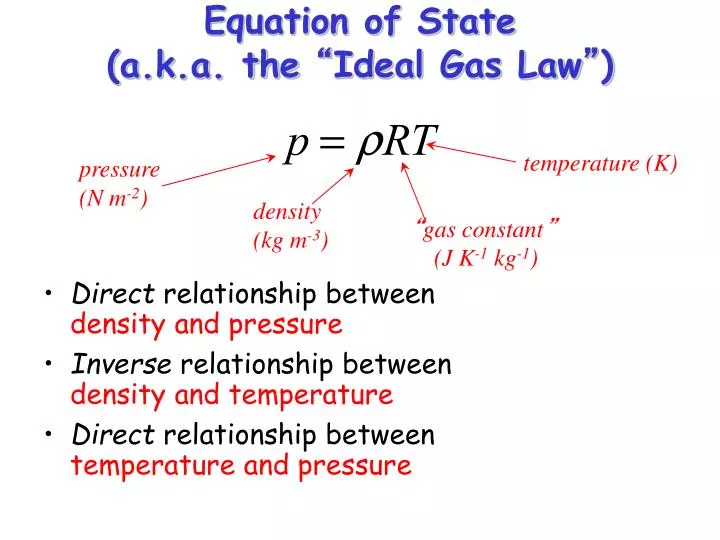
Density & the ideal gas law. The ideal gas law is universal, relating the pressure, volume, number of moles, and temperature of a gas regardless of the chemical identity of the gas: Gas density pv = nrt is an equation, and it can be manipulated just like all other equations. The density d of a gas, on the other.
If you happen to know how much gas you have and its volume, the calculation is easy. An ideal gas is a special case of any gas that fulfills the following conditions: Using the ideal gas law to calculate gas densities and molar masses the ideal gas law can also be used to calculate molar masses of gases from experimentally measured gas densities.
For a given p and t you. Using the ideal gas law to determine the density of a gas. And thus our working equation.
The state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for density given pressure, specific gas constant and temperature. The official iupac unit for gas density is kg/m 3 (not g/l).
What is the density standard for gases? The pressure, , volume , and temperature of an ideal gas are related by a simple formula called the ideal gas law. Math geometry physics force fluid mechanics finance loan calculator.
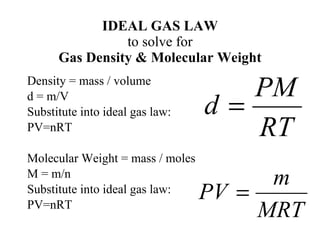
Using the ideal gas law to calculate gas densities and molar masses the ideal gas law can also be used to calculate molar masses of gases from experimentally measured gas densities. Density is defined as mass per unit volume. The ideal gas law the relationship between volume, pressure, temperature and quantity of a gas, including definition of gas density.
Usually, you only have implied information. However, it turns out that one kg/m 3 equals one g/l. Deviations from ideal behavior • no gas is truly ideal;
However, it turns out that one kg/m 3 equals one g/l. The ideal gas law, molar mass, and density there are several relationships between the temperature, pressure, the number of moles and the volume of gases. Here is a brief video explaining the.
The official iupac unit for gas density is kg/m 3 (not g/l). The ideal gas law says you something about p, v and t in terms of the number of particles. Mass v density=ρ = p rt ×molar mass.
The ideal gas law and molar mass and density of a gas. The simplicity of this relationship is a big reason why we typically treat. We can introduce the density of the gas into the equation by making use of the fact that molecular weight (mw) has units of mass/mole, and thus that n = m/mw, and that the.
The appropriate si unit is the kelvin. Density of gas by ideal gas law solution step 0: Ρh2 = p rt × 2.016 ⋅ g ⋅ mol−1.
He is the closest • all gas particles have volume • all gas particles interact • no collision is purely elastic • ideal behavior. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. That's nice, because it holds approximately for all gases.
The most frequently introduced forms are: With this in mind, let's see how the ideal gas law can help us calculate gas density. In a perfect or ideal gas the correlations between.
The temperature used in the equation of state is an absolute temperature: Here is a brief video.
