But only if the naoh is the limiting reactant. There are two types of buffer solutions… acidic buffer acid.
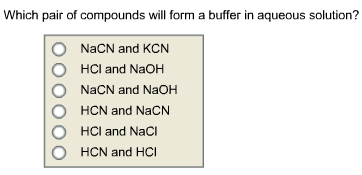
Which Pair Of Compounds Will Form A Buffer In Aqueous Solution? Nacn And Kcn Hcl And Naoh Nacn - Home Work Help - Learn Cbse Forum
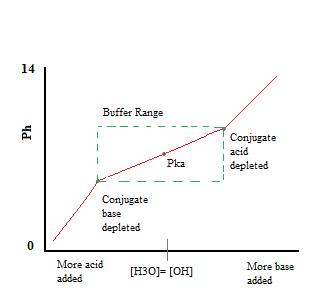
A buffer solution (more precisely, ph buffer or hydrogen ion buffer) is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa.

What forms a buffer. A buffer is a mixture of a weak base and its conjugate acid mixed together in appreciable concentrations. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, thus. It is usually located in the ram.
In general, a buffer solution may be made from known quantities of a weak acid and a salt of the weak acid. Here is an example of a weak. Stoddardtutoring brings you explanations how naoh and hf mix to form a buffer.
A buffer is a temporary holding area for data while it's waiting to be transferred to another location. If your experimental design requires the use of a metal, then you should choose a. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in ph on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali.
Answer 2 ( expert verified ) buffer solutions consist of an aqueous solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. They act to moderate gross changes in ph. The concept of the buffer was.
Simply put, a buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Online buffering happens while streaming music and videos before they play. There are two buffer forms, acid buffer, and base buffer.
Buffering lets you watch or listen to media almost instantly by downloading a small portion. What is a buffer solution? Acidic buffer solutions an acidic buffer.
Acid buffer a buffer solution that contains large quantities of a weak acid, and its salt with a strong base, is called an acid buffer. A buffer solution (more precisely, ph buffer or hydrogen ion buffer) is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. Buffer solution definition in chemistry, the definition of a buffer is a solution that can resist ph change upon the addition of an acid or a base.
A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant ph for the reaction. As a result, buffer solutions usually consist of a mixture of weak acids and their conjugate bases and weak bases and their conjugate acids. It consists of a solution of a weak.
A temporary area of memory or data storage that is used to execute a process. This is why there are a wide variety of possible mixtures that can. Definition a buffer solution is one which resists changes in ph when small quantities of an acid or an alkali are added to it.
Buffer solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid, or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the. A buffer is a solution that can resist ph change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. As previously mentioned, a buffer is a solution of either a weak acid and its salt, or a weak base and its salt.

Buffer Calculations For Polyprotic Acids A Polyprotic Acid Can Form Buffer Solutions In Presence Of Its Conjugate Base. For Example, Phosphoric Acid Can. - Ppt Download