The strongest oxidizing agents taking into account these parameters of the chemical elements, it is possible to. What determines the strength of reducing and oxidizing agents?
We can solve the problem in one of two ways:
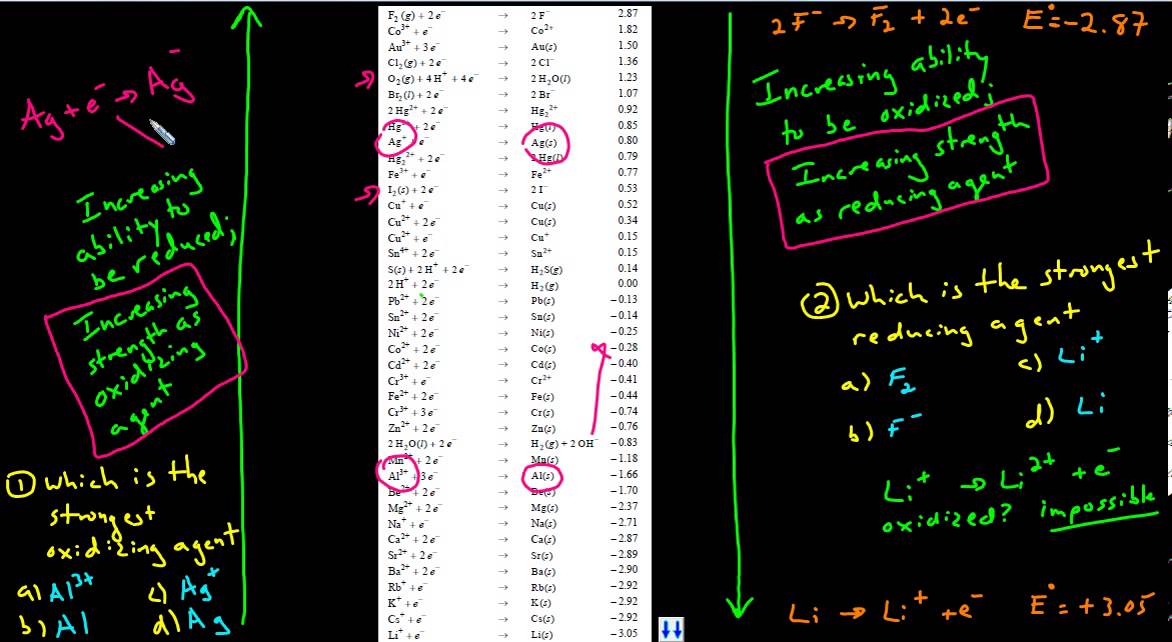
What determines the strength of oxidizing agents. Oxidizing agents normally exist in their highest possible oxidation states and, therefore, have a strong tendency to gain electrons and undergo reduction. You then look at the value of e knot for each equation and see which oxidizing agent resulted in the highest e knot value. Here's a typical table of standard reduction potentials.
Ions, atoms, and molecules having a. The strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents are indicated by their standard electrode potentials. The oxidation and reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons during the reactions.
About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features press copyright contact us creators. It’s also significantly safer to use. The oxidizing agent typically takes these electrons for itself, thus gaining.
The best reducing agents are located at the bottom left of the periodic table (low electronegativity) and the best oxidizing agents are located at the top right of the periodic. (1) compare the relative positions of the four possible reductants with that of the ag 2 s/ag couple in table 19.2 standard potentials. To clearly determine which is the oxidizing agent,.
Being a strong oxidizing agent, chlorine will react with any organic molecule including proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids to disrupt their structure. The higher the pull for electrons the. Elemental fluorine, for example, is the strongest common oxidizing agent.
The higher the electronegativity the greater the pull an oxidizing agent has for electrons. Oxidizing agents increase in strength moving from left to right across the periodic table and from bottom to top,. How do you determine which oxidizing agent is stronger?
The basic fact is ranking of oxidizing and reducing substances in terms of their strength for oxidation and reduction in a chemical reaction depends on their relative ability to. Hydrogen peroxide (h2o2) has an oxidizing potential of 0.70 volts in its aqueous form. An oxidizing agent is a reactant that removes electrons from other reactants during a redox reaction.
Unlike sulfuric acid, hydrogen peroxide is a stronger oxidizing agent. (from wps.prenhall.com) the species at the top left have the greatest potential to be reduced, so. Let's consider standard potentials of some redox couples:
In this case, the noble gases have large values of ionization energies. Following are the common reducing agents, sodium borohydride. The best reducing agents are located at the bottom left of the periodic table (low electronegativity).
The highest e knot value means the oxidizing agent is the. Atoms, ions, and molecules that have an unusually large affinity for electrons tend to be good oxidizing agents. (1) compare the relative positions of the four possible reductants with that of the ag 2 s/ag couple in table 1 or (2) compare e° for.
We can solve the problem in one of two ways:
Comparison Between The Strength Of Reducing And Oxidizing Agents - Tutorke