What is the density of the ideal gas? Chemistry lecture that introduced density into the ideal gas law.
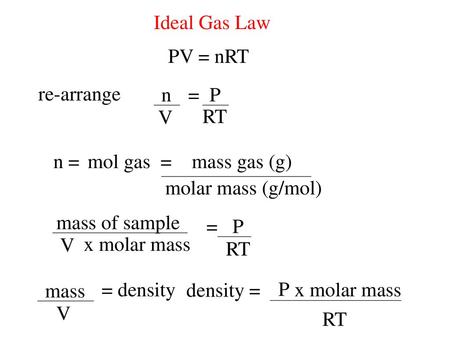
Ideal Gas Law Pv = Nrt Re-Arrange N V = P Rt N = Molar Mass (G/Mol) Mol Gas= Mass Gas (G) Mass Of Sample V X Molar Mass = P Rt =
Here is the ideal gas law equation rearranged to solve for v:

Density and the ideal gas law. Ideal gas molecules do not attract or repel each other. Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for density given pressure, specific gas constant and temperature. However, it turns out that one kg/m 3 equals one g/l.
The ideal gas law is universal, relating the pressure, volume, number of moles, and temperature of a gas regardless of the chemical identity of the gas: Density and specific volume density. The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas.it is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions,.
Absolute pressure (p), volume (v), and absolute temperature (t). Gas density pv = nrt is an equation, and it can be manipulated just like all other equations. Other variations of the ideal gas law are discussed below.
Here is a brief video. Deviations from ideal behavior • no gas is truly ideal; An ideal gas can be characterized by three state variables:
He is the closest • all gas particles have volume • all gas particles interact • no collision is purely elastic • ideal behavior. Density of a gas is generally expressed in g/l (mass over volume). The density d of a gas, on the other.
The only interaction between ideal gas. Math geometry physics force fluid mechanics finance loan calculator. Calculation of density of an ideal gas.
The density is defined as the ratio of the mass to the volume. The term ideal gas refers to a hypothetical gas composed of molecules which follow a few rules: The ideal gas law can be expressed with the individual gas constant.
Ideal gases versus real gases. What is the density standard for gases? The original ideal gas law uses the formula pv = nrt, the density version of the ideal gas law is pm = drt, where p is pressure measured in atmospheres (atm), t is.
Multiplication of the left and right sides of equation 5.5.1 by the molar mass in g/mol ( m) of the gas gives. The official iupac unit for gas density is kg/m 3 (not g/l). To find the density of the gas, you need to know the mass of the gas and the volume.
The ideal gas law, molar mass, and density there are several relationships between the temperature, pressure, the number of moles and the volume of gases. P v = m r t (4) where p = absolute pressure [n/m 2 ], [lb/ft 2] v = volume [m 3 ], [ft 3] m = mass [kg], [ slugs] r =. By doing some algebra, the ideal gas equation can be rearranged to include density.
The relationship between them may be deduced from kinetic. We can introduce the density of the gas into the equation by making use of the fact that molecular weight (mw) has units of mass/mole, and thus that n = m/mw, and that the. Molar volume molar volume vm is defined as the volume of gas per unit mole.
The density of an ideal gas depends on the. With this in mind, let's see how the ideal gas law can help us calculate gas density. Density of gas by ideal gas law solution step 0:
The ideal gas law applies to ideal gases.an ideal gas contains molecules of a negligible size that have an average molar kinetic energy.

Imp Ideal Gas Law And Density | Ideal Gas Law, Physics And Mathematics, Physics Formulas
The Ideal Gas Law: Density Video Tutorial & Practice | Pearson+ Channels
