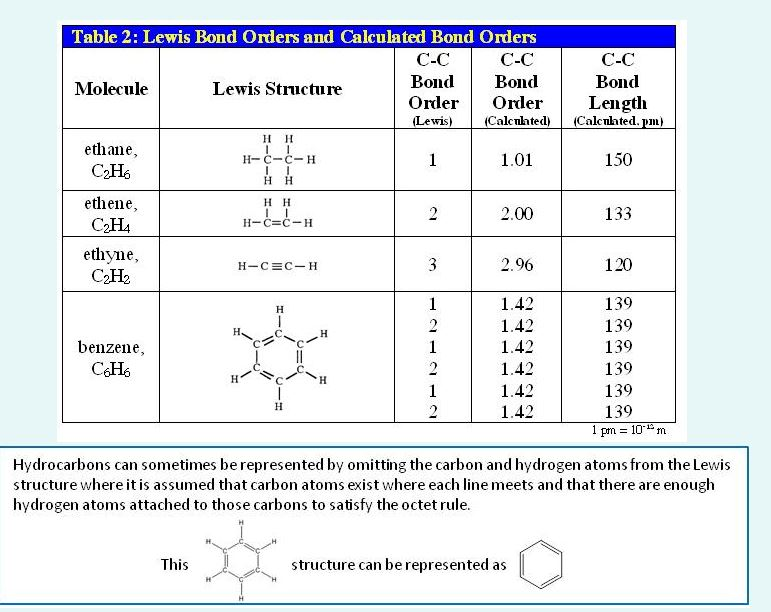
In this compound, 6 pi electrons are shared by 6 carbon atoms; Each carbon atom form one sigma bond one pi bond with another.

The C-C Bond Order In Benzene Is : - Youtube
The pi bonding electron are delocalized over the entire molecule.

Bond order of two cc atoms in benzene. Bond order and bond length indicate the type and strength of covalent bonds. Answer 4.0 /5 34 brainly user benzene is an aromatic cyclic compound, and hence, has resonance structures. So firstly, we cannot alone past.
Benzene is a hexagonal molecule of six carbon atoms, each of which is bound to six hydrogen atoms. Benzene has 6 molecular π orbitals. It has 2 bonding electrons and 0 nonbonding electrons.
The bond order of a bond is half the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. The average value of the equilibrium c c bond lengths in the benzene moiety of 1 (1.394 (7) and 1.393 å) is slightly longer than in benzene (1.3914 (10) å [30, 58]) by about 0.002 å. Real benzene is a perfectly regular hexagon.
This means that neither structures figure 10.7.2 are correct and the true 'structure' of benzene is a mixture of the two. When electrons are displaced a small amount of energy ‘hv’ is released which makes the carbon atoms in the benzene ring more stable and hence the resonance causes stability of benzene ring. Each c − c σ bond is a localized bond.
Every carbon has half a pi bond and one sigma bond. What is the bond order of the cc bonds in the benzene. Two different types of bond are present in benzene.
Bond order is no.of bonds/no.of centers. In the benzene molecule, carbon atoms form a ring with alternating single and double bonds in between each of them. B cc a ′ = 1.01, w cc a ′ = 0.99, b cc a ′ ′ = 0.45, and w cc a ′ ′ = 0.44;
Indeed, notions of single, double, and triple bonds (with bond orders of 1, 2, and 3, respectively) are introduced very early in the chemical education. This nitrogen is group five and as three. So oxygen is group 62 electrons are involved in this double bond, so we have two lone pairs there.
I have quite a complex structure drawn up on the screen and we will be adding lone pairs looking at the bonding angles around our nitrogen and carbon atoms as well as harmony double bonds we have. Of bonds between two atoms c − c bond order in benzene = 2 2 + 1. The equality of all six cc bond lengths, despite the alternating double and single bonds, and the.
The c − c pi bonds. Thus, the bond order of benzene is 1.5 for each bond. Problems with the stability of benzene real benzene is a lot more stable than the kekulé structure would give it credit for.
For example, in diatomic nitrogen, n≡n, the bond order is 3; Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond. Bond order = total no.
Benzene has two resonance structures, showing the placements of the bonds. 26 the c − c bonds in benzene are 140 p m long which puts them in between single bonds and double bonds (given at 147 − 154 p m and 134 − 135 p m respectively, sourced from here and here) as expected. Of resonating structures total no.
Class class 12 class class 11
Solved Table 2: Lewis Bond Orders And Calculated Bond Orders | Chegg.com