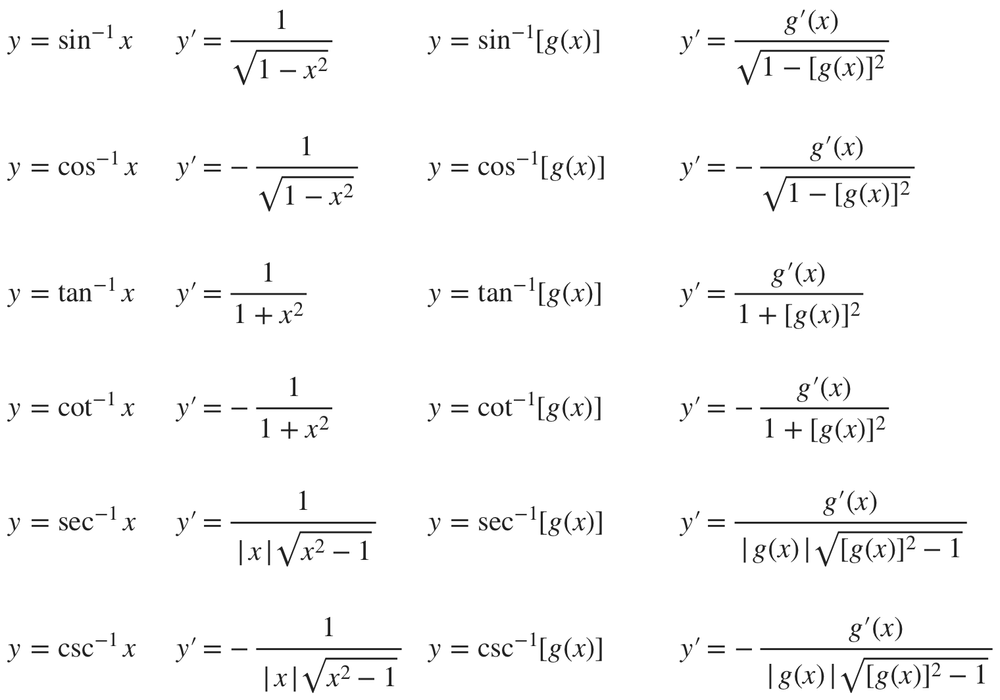For this, let us assume that f (x) = sin x to be the function to be differentiated. The negative sine graph and the positive sine graph have opposite signs:

Differentiation Of Cos Inverse X (Cos^-1 X) - Teachoo [With Video]
D dx [sin( √ex + a 2)] not what you mean?
Derivative of negative sine. We can use the derivative of the sine function in order to compute directly the rate of change, or slope, of the tangent line at this peak on the graph: The derivative of the inverse tangent is then, d dx (tan−1x) = 1 1 +x2 d d x ( tan − 1 x) = 1 1 + x 2. Then f (x + h) = sin (x + h).
Sin’ (π / 2) = cos (π / 2) = 0 we. To remember which derivative contains the negative sign, recall the graphs of the sine and cosinefunctions. The derivative of the sine function d d x [ sin x] = cos x proof:
Now, if u = f(x) is a function of x, then by using the chain rule, we. In other words, it has no antiderivative, or no primitive, or no. It is also known as the delta.
Certainly, by the limit definition of the derivative, we know that d d x [ sin x] = lim h → 0 sin ( x + h) − sin ( x) h recalling the. The derivative of cosine of x is simply the negative sine of x. Then it must be the cases that sin θ = x implicitly differentiating the above with respect to x yields ( cos.
We have to start from the following statement about the limit of trigonometric function f (x) = sin(x) as its. Theorem 3.8 the derivatives of sin x and cos x the derivative of. The derivative of sin x is cos x, the derivative of cos x is −sin x (note the negative sign!) and the derivative of tan x is sec 2x.
Through a verysimilar we can find that the derivative of the cosine function is the negative sine function. From these we may derive the rest of the derivatives, via the quotient and product rules. There are three more inverse trig functions but the three shown here the most.
The function is not the derivative of anything. It says that the derivative of sine is cosine, and the derivative of cosine is negative sine. The first derivative of sine is:
The sine function is said to be. We have already seen that the derivative of the sine function is the cosine function. Derivative of sinx by the first principle.
If we were to follow the same steps to approximate the derivative of the cosine function, we would find that d dx(cosx) = −sinx. When people say “not integrable” they may mean one of several very different things. We are going to use the first principle to find the derivative of sin x as well.
For instance, we can identify the second. So, let's find the derivative of f (x) = sin(x) and then multiply it by −1. Finding the derivative of inverse sine function, d d x ( arcsin x) suppose arcsin x = θ.
Set differentiation variable and order in options. Derivative by the first principle refers to using algebra to find a general expression for the slope of a curve. Cos (x) the first derivative of cosine is:
Atx= 0, sin(x) is increasing, and cos(x) is positive, so it makes sense that the.

Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions | Rules, Graphs & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
Finding Inverse Trig Derivatives — Krista King Math | Online Math Help