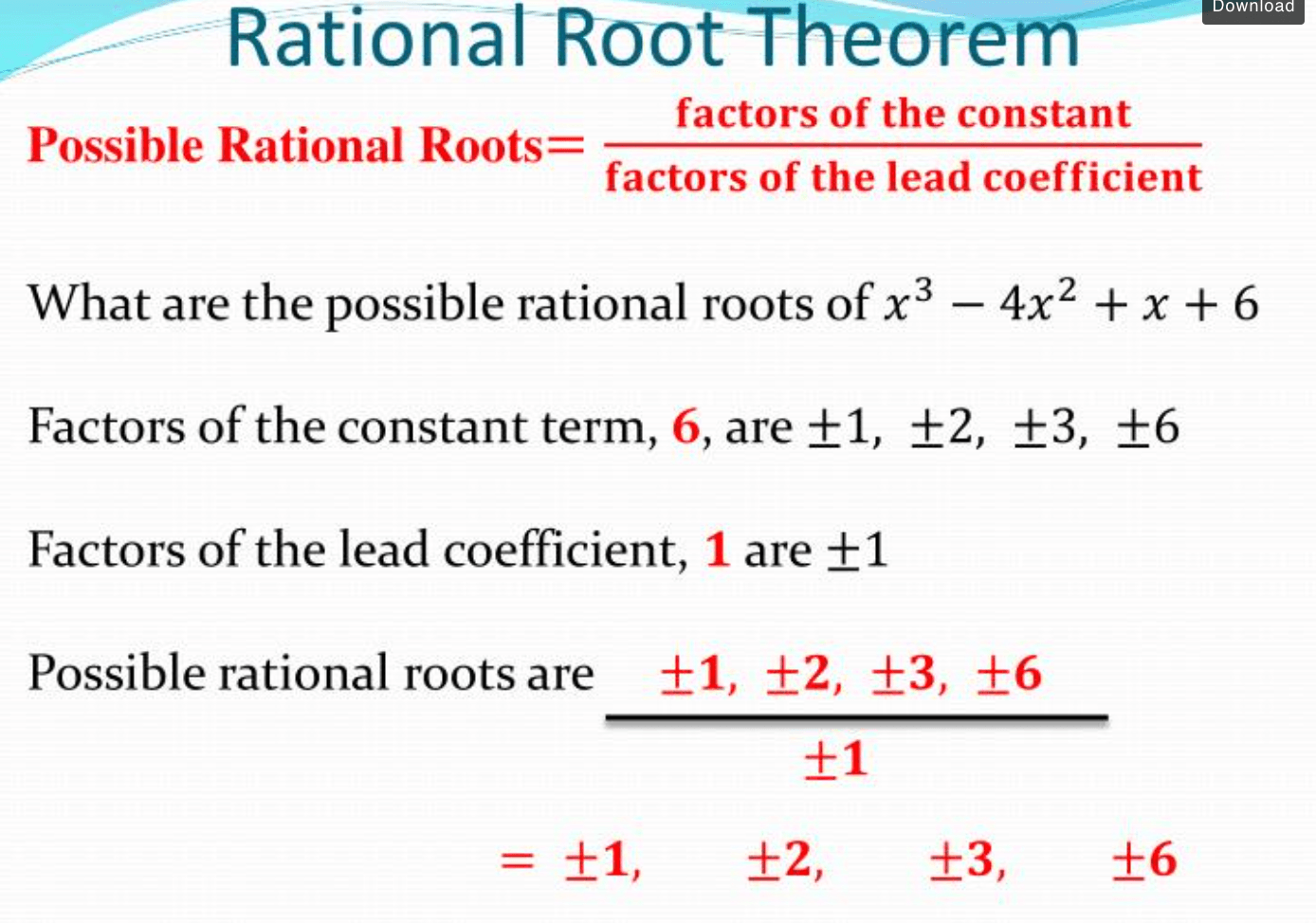
Rational zero theorem if a polynomial function, written in descending order of the exponents, has integer coefficients, then any rational zero must be of the form ± p / q,. Finally, we replace y with f − 1 ( x) which indicates this is the inverse function of the original f ( x).

How Do You Find All The Rational Zeros Of A Polynomial Function? | Virtual Nerd
What is the rational zeros test?

What's a rational zero. When is a rational expression zero? The rational zero theorem is a very useful theorem for finding rational roots. It states that if any rational root of a polynomial is expressed as a fraction eq\frac p q /eq in the lowest.
Arrange the polynomial in descending order. Fraction r/s shows that when 0 is divided by a whole. A rational zero is a zero where the input of the function is rational.
The rational zeros theorem states: In algebra, the rational root theorem (or rational root test, rational zero theorem, rational zero test or p/q theorem) states a constraint on rational solutions of a polynomial equation + + + =. The delhi police recently lodged a ‘zero fir’ against the district magistrate of deoghar in jharkhand on the charge of sedition and under the officials secret acts in the.
If p (x) is a polynomial with integer coefficients and if p q is a zero of p (x) , ( p (p q) = 0 ), then p is a factor of the. Some of the examples of rational numbers are 1/2, 1/5, 3/4, and so on. Apply synthetic division to calculate the polynomial at each value of rational zeros found in step 1.
The set of rational numbers is represented as ℚ. List down all possible zeros using the rational zeros theorem. To find the values that make a rational expression zero, we set the numerator equal to zero and.
After that, there are test style practice questions for you!. That means that you can write it as the ratio of two integers. Write down all the factors of the.
F ( x) = x − 8. − 3 x + 4. A real zero is a zero where the input of the function is a real.
The rational zero theorem states that each rational zero (s) of a polynomial with integer coefficients f (x) = anxn +an−1xn−1+.+a2x2 +a1x+a0 a n x n + a n − 1 x n − 1 +. We can use the rational zeros theorem to find all the rational zeros of a polynomial. We start with a rational function:
This rational expression proves that 0 is a rational number because any number can be divided by 0 and equal 0. A rational expression is zero when the numerator is zero. In this lesson, you will see the rational root theorem, or the rational zero theorem, and how to use it with guided examples.
Rational root theorem, also called rational root test, in algebra, theorem that for a polynomial equation in one variable with integer coefficients to have a solution (root) that is a rational. We solve the new equation for y in terms of x. The number “0” is also a rational number, as we can.
A rational number is defined as a real number in the form of a/b where b is not equal to zero.