There are several types of lipids, of which. Castillo ej, koenig jl, anderson jm, jentoft n:.
Structural Biochemistry/Lipids/Lipid Bilayer - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open World
Nucleic acids, such as messenger rnas, antisense oligonucleotides, and short interfering rnas, hold great promise for treating previously 'undruggable' diseases.

Protein vs lipid. If you’re looking for the difference between peptides and proteins, the short answer is ‘size’. In published literature it seems that the standard protocol is to use the. They are carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
The shape determines the protein’s role. Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins (lipoproteins) in the circulation. What is the difference between lipids and protein?
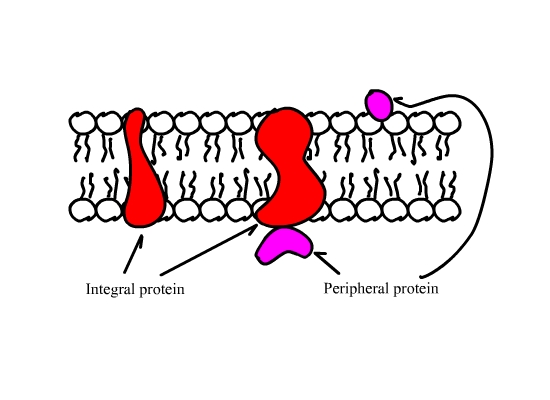
Encompassing carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids, macromolecules exhibit a number of similarities. Membrane proteins can be associated with the lipid bilayer in various ways. Gram for gram, lipids — like butter and oils — provide more than twice as many calories as other macronutrients (both carbs and protein), at 9 calories per gram,.
When you digest protein, it’s broken down into individual amino acids that your body uses to build new proteins. They can also be found in cells and tissue throughout your body. Considering their functions, the difference between carbohydrates and lipids is that the lipids involve in cell signalling processes while carbohydrates do not.
A carbohydrate consists of carbon (c), hydrogen (h), and oxygen (o) atoms, usually. This information will then be linked to pollinator communities and rate of visitation to each of the plant species. For example, all except lipids are long chains made up of.
Lipids contain 3 elements c, h and o while protein contain c,h,o,n and s ( in few). They can be divided into three categories. Different membrane proteins are associated with the membranes in different ways, as illustrated in.
The unit of lipids is triglyceride which contains. A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other.

Protein, Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acid Elements Of Biological Molecules - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com

Protein, Carbohydrate And Lipid Metabolism And Communication In Fish.... | Download Scientific Diagram