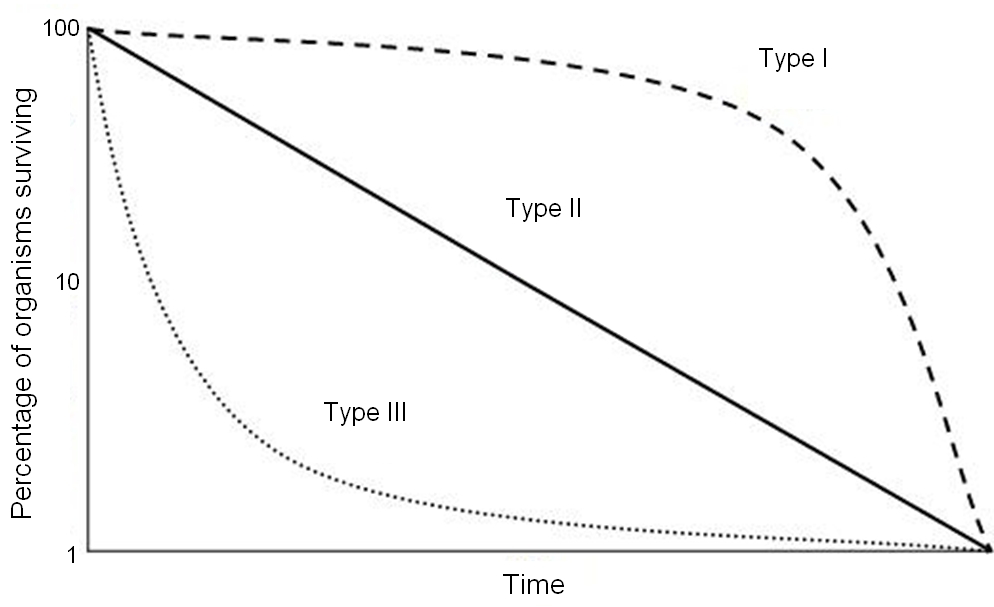
The r selected species live in populations that are highly variable. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Difference Between R And K Selection
Then, what is the difference between k and r selected species?
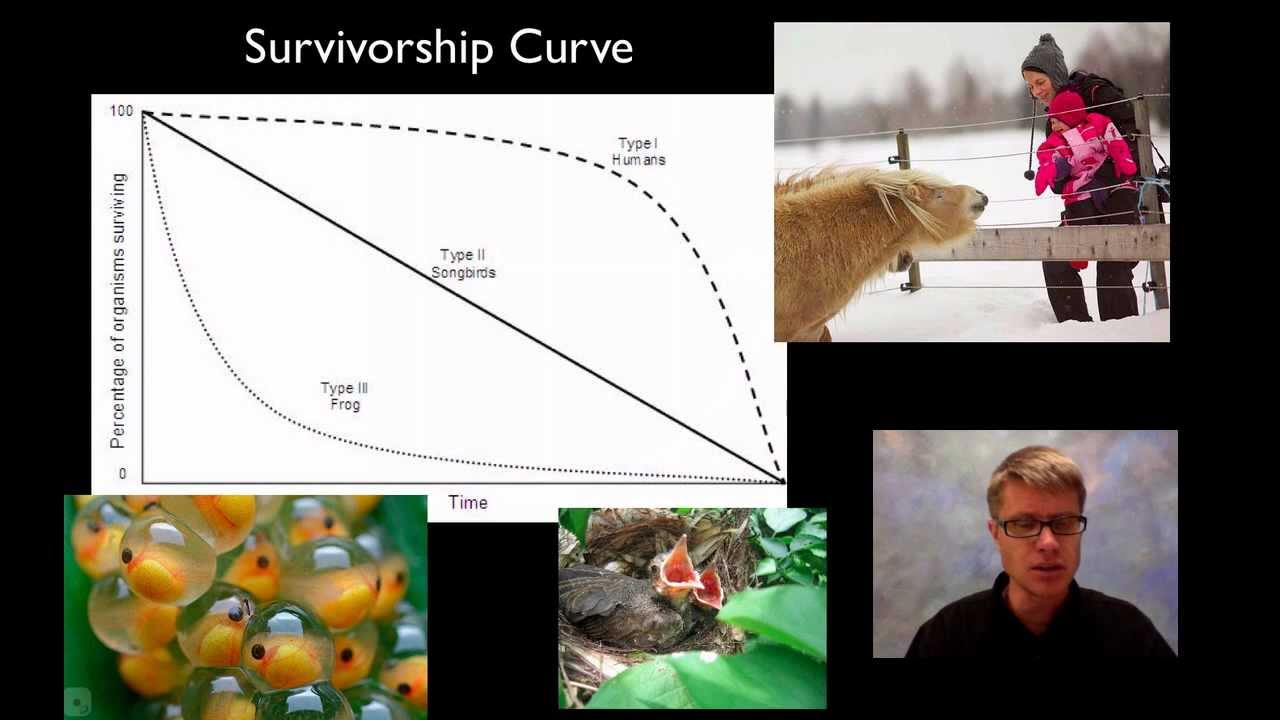
Humans reproduce in k-selected or r-selected. Iteroparous vertebrates include birds, reptiles, fishes, and mammals (angelini and ghiara 1984). 1 answer david drayer nov 26, 2017 r/k selections is a theory that organisms either survive by r the rate of reproduction or k the level of care provided to offspring. They produce, during their life spans, fewer progeny, but place a greater investment in each.
In k selected species, population size are often small, and therefore, individuals run a high risk of inbreeding. Humans fall into the k part of the theory. They tend to be smaller organisms, so the energy used to make each individual is low, and they live in unstable environments.
They also have shorter lifespans and reach sexual maturity quickly. Their reproductive strategy is to grow slowly, live close to the carrying capacity of their habitat and produce a few progeny each with a high probability of survival. Reptiles and turtles have both r and k while male humans have r and females have k.
Humans fall into the k part of the theory. The r selected species live in populations that are highly variable. The fittest individuals in these environments have many offspring and reproduce early.
Train stations near reprodução humana fmabc in santo andr. The fittest individuals in these environments have many offspring and reproduce early. Are humans semelparous or iteroparous?
Short gestation, short parental care and a short time until the off spring can reproduce. Subsequently, question is, are trees k selected species? Breeding only once or twice in their lives having a huge number of offspring.
Difference between r selection and k selection as a reproductive strategy the r and k classification was originally proposed by the biologists robert mcarthur and e. The fittest individuals in these environments have many offspring and reproduce early. The r selected species live in populations that are highly variable.
The theory was developed by studying succession. This would be seen in rodents with many offspring. In k selected species, population size are often small, and therefore, individuals run a high risk of inbreeding.
Also know, what is the difference between r selected and k selected species? R/k theory was developed in the 1970s and was popular in the 1980s and 1990s. Small size of both offspring and adults minimal parental care before reaching reproductive maturity high infant mortality.

Life-History Traits Of R-And K-Selected Species (Combined | Download Table