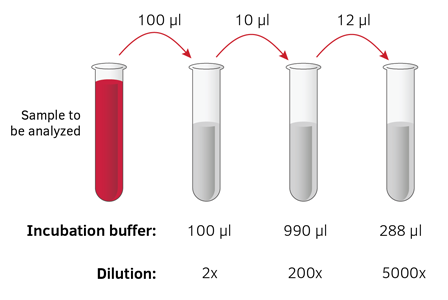
The progression of calibration standard concentration is always a geometric series. The formula for calculating a dilution is (c1) (v1) = (c2) (v2) where.
Dilution factor = v2/v1 10 0 fold 100 fold 10 fold 10 fold.
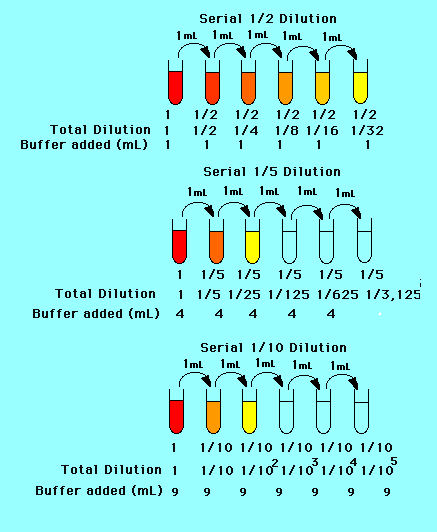
Calculations for a serial dilution. A serial dilution is a series of dilutions made sequentially, using the same dilution factor for each step.the concentration factor is the initial volume divided by the. V1 is the volume of the starting solution. A solution of lower concentration is made by diluting a calculated volume of a solution of higher concentration with solvent (most commonly water) up to a specified volume (the volume of the.
In serial dilutions, you multiply the dilution factors for each step. 1, x10, x100, x1000, x10000 b measure 11 cm 3 of your starting solution into the. How to calculate dilution factor?
Serial dilutions are made by making the same dilution step over and over, using the previous dilution as the input to the next dilution in each step. As a pharmacy student, it’s vital, then, that you have a solid understanding of the implications that a dilution has, and how to. To determine the concentration at each step of the series, you divide the.
Serial dilution can be used for. We would like to count the bacteria in a particular sample, and we think that there should be in the neighborhood of 10. The sample/culture is placed in a test.
To make a dilution series, use the following formulas: The dilution factor or the dilution is the initial volume divided by the final volume. Df = v i v f for example,.
If the dilution factor is in the form of a fraction, flip the fraction (i.e., 1/50 becomes multiply by 50/1). With the dilution of a medicine, drug concentration changes. Take 7 clean and sterile test tubes.
The ratio of the final volume to the aliqout volume of the stock is known as dilution factor (df). C1 is the concentration of the starting solution. The dilution factor chosen for the series of calibration standards is achievable by using serial dilution.
Total dilution factor = df x df ect 102 104 105 106. C2 is the concentration of the. Using serial dilution to count bacteria so let's put this all together.
Serial dilution calculations in microbiology in a microbiology laboratory, in order to determine the number of cells in a sample, the serial dilution method is performed so that. And perform serial dilution calculations. A consistent quantity of sterile diluent, such as distilled water or 0.9 percent saline, is used to dilute a sample during the serial dilution.
If the dilution factor is in decimal form, multiply by 1 over the decimal (i.e., 0.02 becomes. To dilute a stock solution, mix the stock solution with diluent. Total mixing volume = diluent.

Serial Dilution Method & Purpose | What Is Serial Dilution? - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com