Follow report by divrajtharol2138 24.08.2018 log in to add a comment The genes coding for small subunit of 18s ribosomal dna (rdna) are used in molecular taxonomy studies because, mutations are unlikely to survive natural selection and these genes have very less mutations.
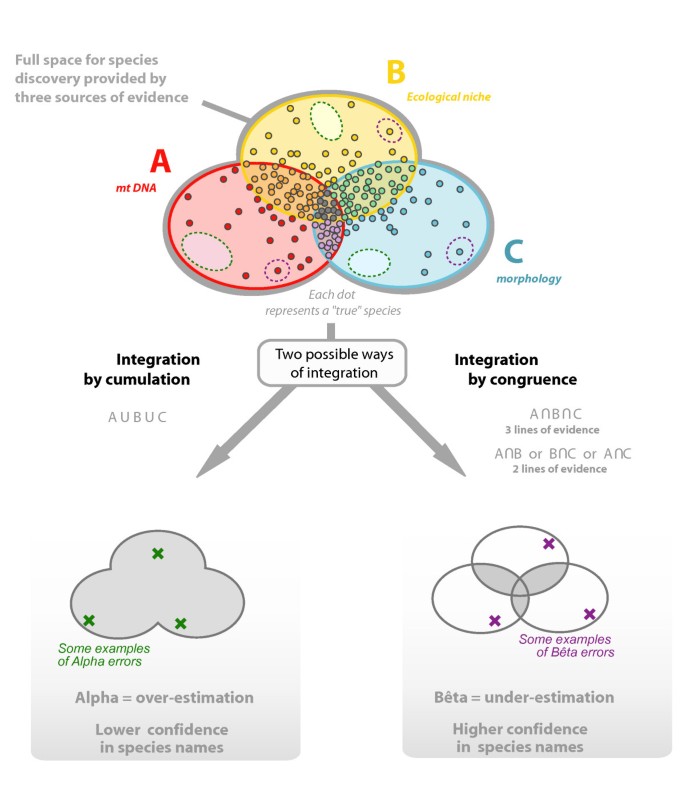
The Integrative Future Of Taxonomy | Frontiers In Zoology | Full Text
(ii) in the rickettsiales, members of the genera anaplasma, ehrlichia, cowdria, neorickettsia and wolhbachia are so closely related phylogenetically on the basis of 16s rrna sequences, and for some also of groesl operon sequences, that they have recently been fused, correctly so, into one family, the anaplasmataceae, while the tribes ehrlichieae.

Molecular characters in taxonomy. Molecular methods of species delineation are rapidly developing and widely considered as fast and efficient means to discover species and face the 'taxonomic impediment’ in times of biodiversity crisis. Molecular phylogenetics and what taxonomy is the course about ø what is molecular phylogenetics, The dna sequence clusters are indicative of the.
In this study, we use pholcid spiders in an effort to address two main issues. The identification of species using molecular characters is a promising approach in alpha taxonomy and in any discipline depending on reliable assignment of specimens. History of taxonomy the classification and naming of organisms is an ancient endeavour.
Molecular taxonomy is particularly effective in combination with other methods, usually with morphology. Often guanine to cytosine (gc) ratio of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is also used. However, molecular systematic investigations of subgroups revealed that current taxonomy is at odds with evolutionary relationships.
Molecular phylogenies support homoplasy of multiple morphological characters used in the taxonomy of heteroscleromorpha (porifera: So far, however, this form of dna taxonomy frequently remains incomplete, lacking the final step of formal species description, thus enhancing rather than. Major characteristics used in microbial taxonomy.
Cluster of sequences called 'molecular operational taxonomic units' (motu) are obtained by grouping sequences of a conserved region or gene fragment. Molecular genetic methods provide taxonomy with a powerful tool to identify or describe species, as they apply to all organisms and offer quantifiable characters. Evaluation of species identification methods using co1 and 16s rrna.
Tropical members of the family remain particularly understudied, including the large genus phyllopsora. Classical and molecular characters in taxonomy ask for details ; Taxonomically important morphological, cultural and.
Historically, generic boundaries in the ramalinaceae were primarily based on morphological characters. Classically, the bacteria have been classified on the basis of similarities in phenotypic characteristics, like morphological features, response to gram stain, cultural characteristics, physiological biochemical properties, pathogenicity, antibiotic sensitivity, serological relationships etc. Molecular taxonomy in pholcid doi:
Molecular taxonomy is a robust classification system that continues to enhance our understanding of bacterial evolution and redefine the tree of life. Phylogenetic relationships were inferred from nucleotide sequences in the its regions and 5.8s gene of the rdna under four optimality criteria: If two organisms that are thought to be closely related, based on phenotypic criteria, do not have similar gc values, then they are not in fact closely related.
It is a means of assigning an organism to a specific. The following are the molecules used in the molecular taxonomical studies. Previous studies have shown the feasibility of the method, but considerable controversy persists.
A molecular phylogenetic analysis was conducted on 32 species of pestalotiopsis in order to evaluate the utility of morphological characters currently used in their taxonomy.