When you see limit, think. L = lim x → 0 ln x = lim x → 0 x ln x x = lim x → 0 ln x + 1 1 = l + 1 which implies that l = ± ∞ now just show ln ( x) is decreasing to prove that l = − ∞ share answered jul 3,.

Top 18 Ln Limit To Infinity En Iyi 2022
What is the limit as x approaches the infinity of ln (x)?
Ln approaches infinity. The limit of 1 x as x approaches infinity is 0. Find the limit of (ln (x)/x as x approaches \infty. And write it like this:
As x approaches positive infinity, ln x, although it goes to infinity, increases more slowly than any positive power, xa (even a fractional power such as a = 1/200). If x >1ln (x) > 0,. The opposite case, the natural logarithm of minus infinity is undefined for real numbers, since the natural logarithm function is undefined.
The natural logarithm of zero is undefined: The ln of 0 is infinity. Lim x→∞ ( 1 x) = 0.
The limit of this natural log can be proved by reductio ad absurdum. X x approaches infinity is the ratio of the coefficients of their highest degree terms. The answer is +∞ you can prove it by reductio ad absurdum.
Lim ln(x) = ∞ x→∞. Lim x → 0 ln ( x 2) = lim y → 0 + ln y = − ∞. The limit near 0 of the natural logarithm of x, when x approaches zero, is minus infinity:
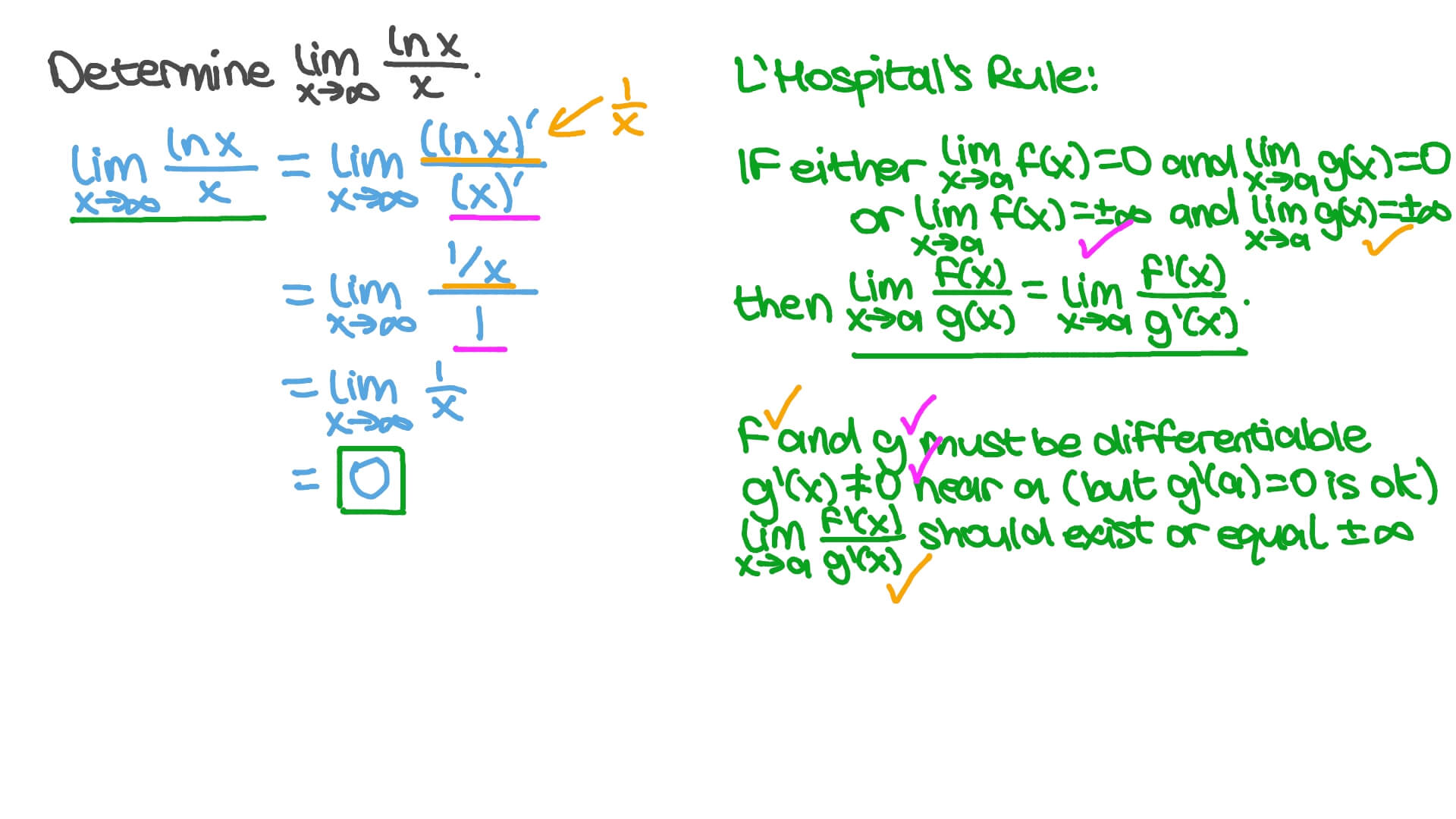
We want to determine the value of \displaystyle \lim_x \to \infty \dfrac\ln xx^{\frac{1}{3}}. Calculus evaluate the limit limit as x approaches infinity of ( natural log of x)/x lim x→∞ ln(x) x lim x → ∞ ln ( x) x apply l'hospital's rule. When we substitute x = \infty, we see that the function approaches.
Lim x→∞ 1 x lim x → ∞ 1 x. Learn how to solve limits to infinity problems step by step online. As x approaches infinity, then 1 x approaches 0.
If we directly evaluate the limit \lim_ x\to \infty \left (\frac \ln\left (x\right). You know that if x > 1ln(x) > 0 so the limit must be positive. The limit as x approaches infinity of ln (x) is +∞.
For example, in this problem, the highest degree of x x in both the numerator and denominator. Note that ln ( x 2) is defined for any x ∈ r ∖ 0 and therefore the limit exists, indeed just take y = x 2 → 0 + then. No, the logarithm of 0 (to any base) does not exist.
You also know that ln(x2) − ln(x1) = ln( x2 x1) so if x2. In terms of the limit we might say that ln (x) goes to negative infinity as x goes to 0. Practice your math skills and learn step by step with our math solver.
Without Using The L'hospital's Rule, How Do I Solve The Limit Of [Math]\FracLn(2^X+3^X)X[/Math] As X Approaches Infinity? - Quora
L'hopital On Limit Of Tanx(Lnx) As X ->0 (From The Right). | Physics Forums